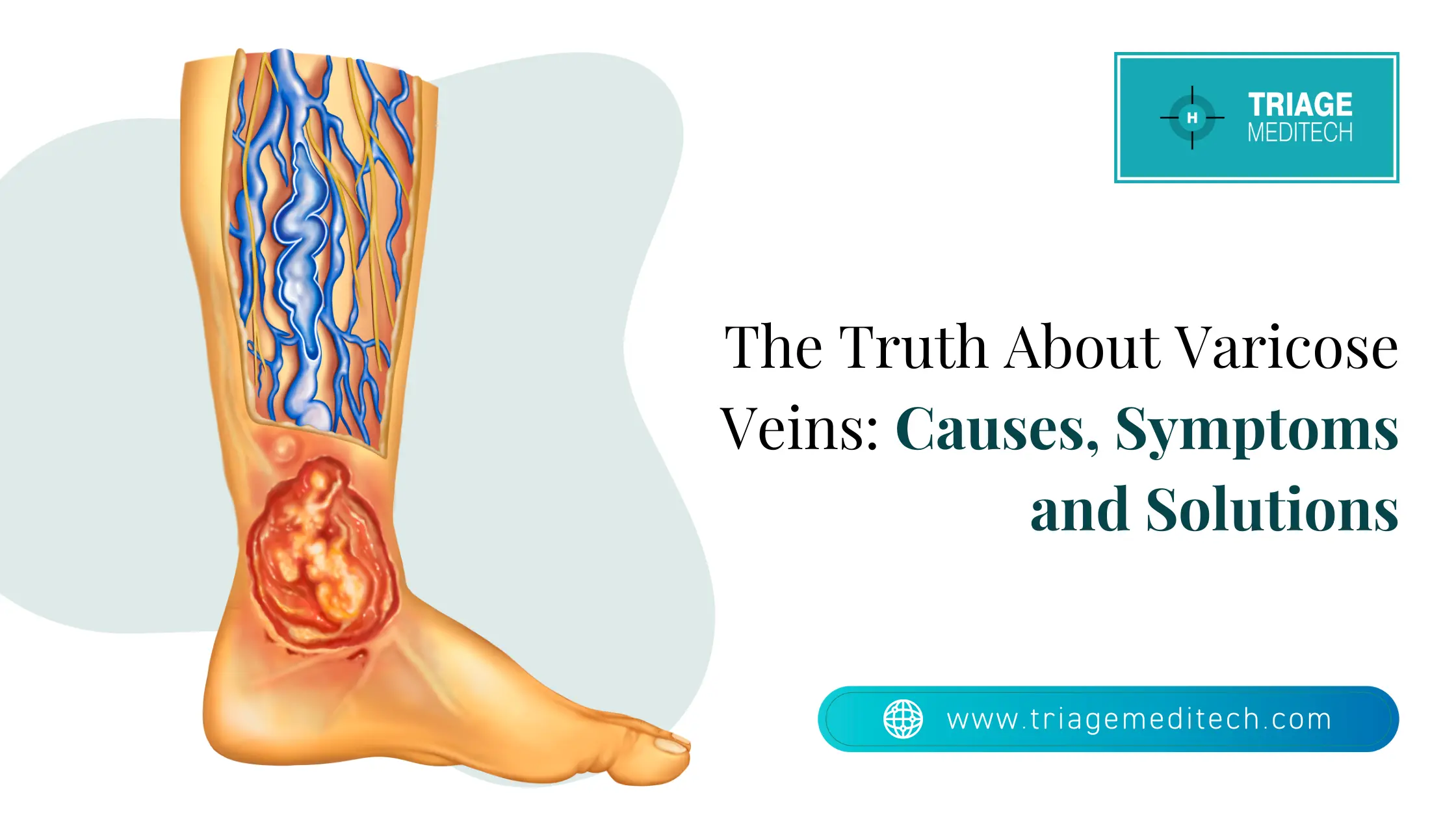
The condition affects numerous people across the world because it creates discomfort and affects the appearance of patients. The guide provides an extensive understanding of varicose veins by defining their characteristics and causes and symptoms, and stages of progression, together with various management approaches, including medical interventions. The following content will teach you how to detect early warning signs and avoid complications while guiding your vascular health choices.
What Are Varicose Veins?
The medical condition known as varicose veins, also known as varicoses, appears as enlarged, twisted veins that are more than 3 mm in diameter and display blue or purple colouration, mainly affecting the leg area. The condition develops through weakened vein walls, which lead to malfunctioning valves, resulting in blood accumulation and swollen veins. The condition of varicose veins develops as a result of genetic factors and pregnancy complications and obesity, ageing, as well as prolonged standing. The symptoms of this condition consist of painful legs and swollen legs with a heavy feeling and cramping. The lack of treatment could result in the development of blood clots and ulcers. The treatment approaches consist of lifestyle modifications combined with compression stockings and sclerotherapy or laser ablation under the guidance of a vascular surgeon for achieving the best results.
The Science Behind It
The circulatory system depends on valves in veins to maintain one-way blood flow because these veins direct blood toward the heart. Vein enlargement occurs because of failing valves and weakened vein walls, which allow blood to accumulate and result in pressure buildup that makes veins bulge. The medical condition venous insufficiency creates varicose veins as which worsen with prolonged standing or sitting.
Causes of Varicose Veins
Several factors contribute to the development of varicose veins, ranging from genetics to daily habits.
Genetics and Lifestyle
Family background strongly influences the risk of developing varicose veins because if your relatives have them, your chance of getting them rises. Genetics plays a role in this condition because people may inherit weak vein walls and malfunctioning valves. The natural process of aging, alongside prolonged standing or sitting, along with sedentary behaviors, causes vein weakening, which makes the condition worse. People working in nursing, teaching, and retail roles who must stand for extended hours face an elevated risk of developing varicose veins. The absence of regular physical exercise creates obstacles for blood flow, which causes excessive strain on the vein structures.
Risk Factors to Watch For
In addition to lifestyle factors and genetics, multiple crucial risk elements should be monitored by individuals.
- Age: With time, your veins naturally become less flexible, and your heart valve system weakens, which reduces blood return to the heart. The accumulation of blood leads to the formation of varicose veins.
- Gender: The medical condition varicose veins affects women much more frequently than it does men. The main explanation for this condition lies in hormone transformations which occur at three specific stages of life: puberty and pregnancy, and menopause. The relaxation effect of female hormones on vein walls leads to their increased susceptibility to stretching and weakening.
- Pregnancy: The body experiences significant blood volume expansion during pregnancy that creates added pressure on the veins. The expanding uterus applies pressure to the pelvic area’s large veins while obstructing blood flow from the legs, which increases the risk of developing varicose veins.
- Obesity: When you carry extra weight, your veins in the legs must work harder to fight gravity, which makes blood flow less effective. The elevated blood pressure damages veins while creating varicose veins.
- Inactivity: The lack of movement, together with inactive lifestyle patterns, leads to insufficient blood circulation.
Moving your leg muscles functions as a blood pump, which helps return blood to your heart. Veins become prone to blood pooling because muscle action does not occur, which results in elevated pressure and varicose vein development.
Early Stage Varicose Veins Symptoms
The first signs will allow you to start treating varicose veins before they advance to a more severe stage.
Identifying the Subtle Signs
Early-stage varicose veins produce a heaviness sensation or aching pain that manifests mainly in the legs following prolonged standing periods. Your ankles and feet may show minor swelling, together with tiredness or restlessness in your legs. Early signs of varicose veins often present as a mild itching sensation around the affected vein.
When to Worry About Varicose Veins
You should seek medical attention if your veins remain painful or if your skin experiences persistent itching or colour changes, together with throbbing or cramping. Any bleeding symptoms along with sudden swelling or redness, and heat around the affected vein require emergency medical evaluation because they may indicate blood clot formation.
Varicose Veins Stages
The development of varicose veins progresses through several stages from cosmetic concerns to serious health complications. Early detection and effective management of the condition require stage understanding because untreated varicose veins will progress to cause more discomfort along with additional health complications.
Stage 1 of Varicose Veins: Mild Discolouration and Swelling
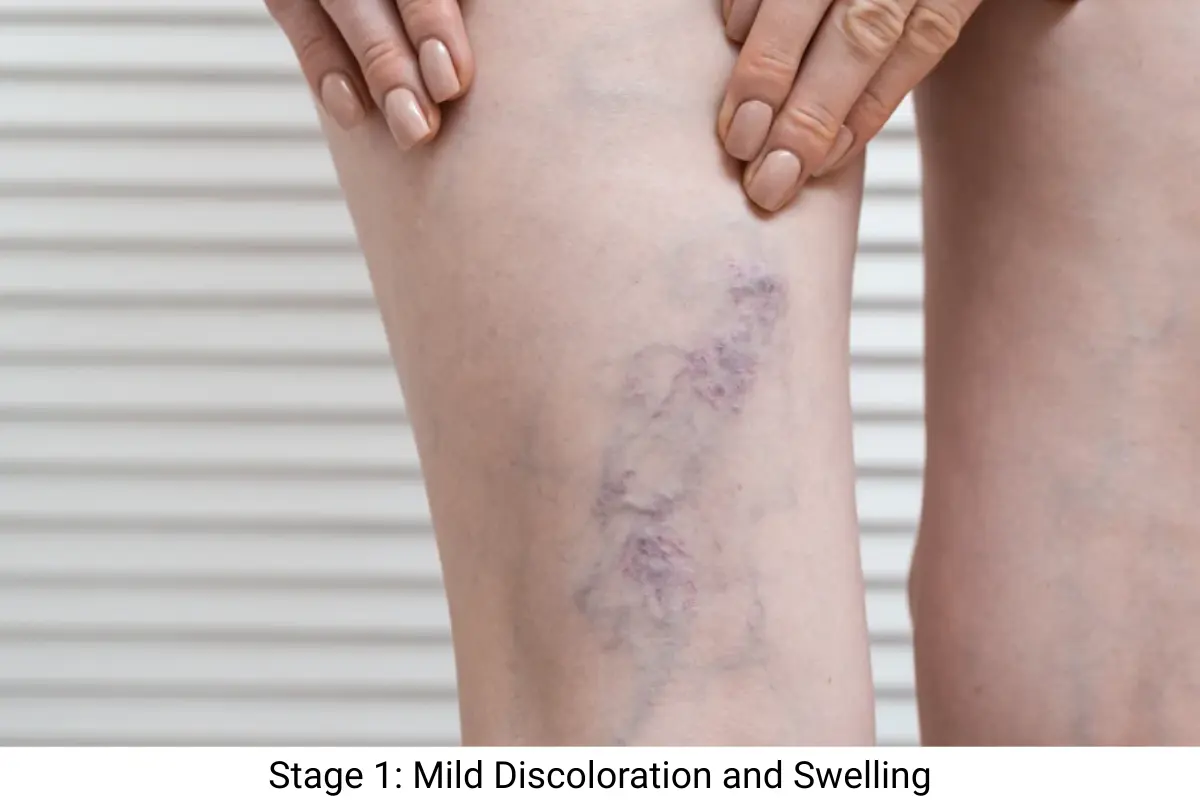
During the first stage of varicose veins appearance, you will notice spider veins or smaller varicose veins. The symptoms in this stage include light swelling and weight feelings and occasional discomfort, and itching, but they remain controllable and do not cause severe disability.
Stage 2 of Varicose Veins: Aching and Bulging Veins
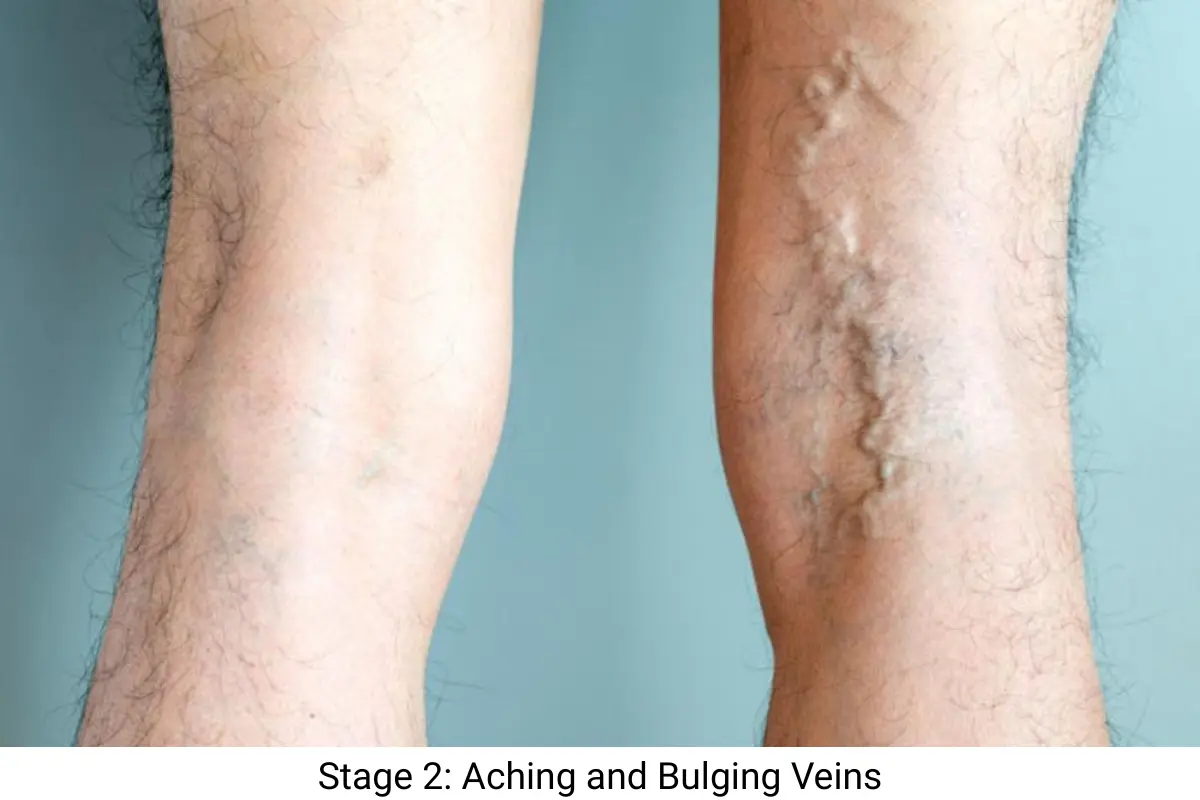
The veins expand in size while the condition advances to its next stage. Standing for extended periods makes the aching pain and throbbing more intense. During this phase, you will experience night cramps alongside increased swelling in your ankles and feet.
Stage 3 of Varicose Veins: Skin Changes and Ulcers
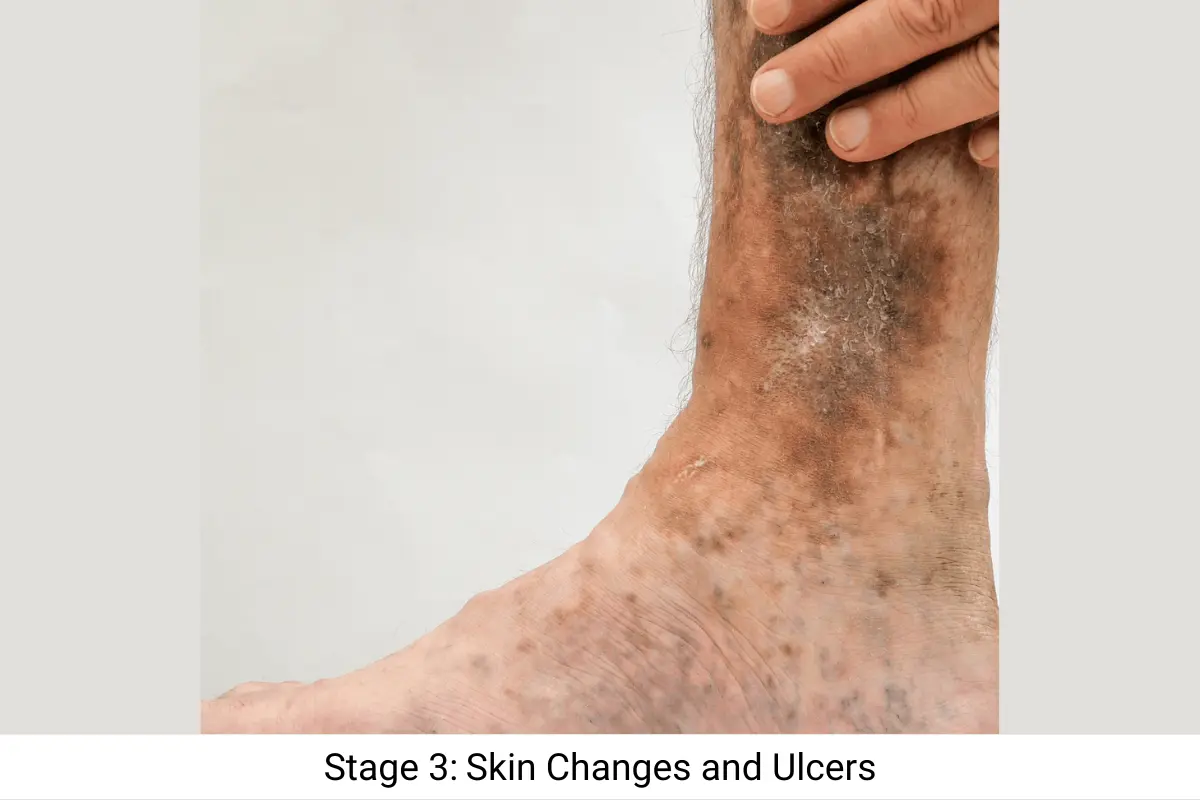
Chronic venous insufficiency advances to cause significant changes in skin appearance. The skin surrounding varicose veins develops brownish discoloration and becomes hardened, while also becoming dry and itchy. The most serious complication of venous insufficiency occurs when it produces venous leg ulcer that develops around the ankle area and heals slowly. Such conditions show severe vein damage that needs immediate medical intervention.
Spider Veins vs Varicose Veins
The two vein conditions differ substantially despite their shared connection to vein damage. The appearance of spider veins consists of small web-like patterns that remain painless and show red or blue colors beneath the skin. The appearance of varicose veins presents as large bulging structures, which typically cause pain through heaviness or aching sensations. The distinction between these conditions enables you to select the most suitable treatment method.
Spider Veins vs Varicose Veins: What’s the Real Difference?
Spider veins exist as thin web patterns that appear only as a cosmetic issue without causing discomfort. Varicose veins develop into large, painful structures that may create health problems when not treated properly. Both can be treated, but varicose veins often require more intensive interventions. That’s the real difference between spider veins vs varicose veins.
Compression Socks for Varicose Veins
For varicose veins and their symptoms, compression socks are a commonly recommended non-invasive treatment and are considered garments of a clinical nature. By gently squeezing the legs, they enhance blood flow and alleviate discomfort.
Do They Really Work
Like most garments, compression socks also have their advantages. They help with blood flow and discomfort. They have also been shown to treat early symptoms of varicose veins. The symptoms do not progress if the socks are worn regularly.
Choosing the Right Pair
For optimal compression support, a pair with 15-30 mmHg of compression should be selected. The socks should not be too tight and should be easily breathable for maximum comfort. A medical professional can aid with the proper fitting.
Venous Leg Ulcer
A venous leg ulcer is a serious consequence of advanced varicose veins. They illustrate how impaired function of veins can have serious consequences on the health of the skin and which can lead to a chronic wound.
Why can Untreated Varicose Veins Lead to this?
Chronic venous insufficiency as a result of untreated varicose veins leads to impaired circulation and skin breakdown, leading to venous leg ulcer. Also, these can be open sores that are a source of pain and become infected.
How to Refrain from this Complication
- Use compression hosiery regularly.
- Maintain a healthy weight, as this can put excess pressure on your veins.
- Early treatment could include vascular procedures and/or lifestyle changes for varicose veins.
When to See an Interventional Radiologist?
Whilst it is easy to categorise varicose veins as only a cosmetic issue, it’s not always so black and white. But knowing when they may be a sign of something more serious indicates a need to see an Interventional Radiologist or Vascular Surgeon. This lets you know if it’s safe to monitor the condition and any potential treatments that could be made available to you.
Advise medical help if you find yourself considering any of the following:
- Severe pain or swelling in the legs.
- Skin ulcers or open sores.
- Sudden changes in vein appearance, like redness or warmth, may indicate a blood clot.
Long-Term Prevention Tips
Here are some long-term prevention tips are below:
Diet, Exercise, and Daily Habits
- Diet: Eat fibre-rich foods, like fruits and vegetables, to support healthy blood vessels. Avoid excessive salt to reduce swelling.
- Exercise: Activities like walking, swimming, or yoga improve circulation and strengthen leg muscles.
- Daily Habits: Avoid prolonged sitting or standing, and elevate your legs when resting.
Surgical and Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Here are some surgical and non-surgical treatment options:
Varicose Veins Medical Devices
The world of technology has offered patients better ways to deal with varicose veins with aggressive and less invasive methods.
Latest Innovations in Treatments
Some solutions offered are:
- EVLT or Endovenous Laser Therapy makes use of laser energy to seal the affected vein.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: Heats and closes veins using radio frequency energy.
- VenaSeal: A medical adhesive that seals the veins and redirects blood flow.
Advanced Surgical Treatments
For severe cases, procedures like vein stripping or phlebectomy remove damaged veins. These are typically reserved for advanced stages with significant complications.
Emerging Nonsurgical Instruments
Nonsurgical instruments are becoming more common, like portable ultrasound therapy devices designed to improve circulation and relieve symptoms in the comfort of home! While the research is still ongoing, the idea that accelerating the healing of chronic venous ulcer, through early heavy dependent management, shows promise.
Living with Varicose Veins
While varicose veins can be a persistent challenge, effective strategies exist to alleviate discomfort and improve your quality of life. Embracing proactive measures and daily self-care can significantly help in managing the condition.
Managing Symptoms Day-to-Day
- Wear compression socks during the day.
- Take breaks to elevate your legs or walk.
- Use moisturisers to prevent skin dryness and irritation.
Myths About Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are a common condition, yet numerous misconceptions surround them. It’s important to separate fact from fiction to understand this vascular issue and seek appropriate care.
Busting Common Misconceptions
- Myth: Varicose veins are only a cosmetic issue.
Fact: They can lead to serious complications like ulcers or blood clots if untreated. - Myth: Only older adults get varicose veins.
Fact: Younger individuals, especially those with genetic predispositions, can develop them. - Myth: Crossing your legs causes varicose veins.
Fact: No direct link exists, but prolonged inactivity can contribute.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are not merely a cosmetic issue, and untreated can affect the quality of life. Varicose veins cannot be prevented when the causes, signs, and symptoms are not known; otherwise, patients can live with varicose veins through preventive methods such as lifestyle changes and compression stockings. Using minimally invasive and very safe techniques, one can treat even the advanced forms of varicose veins. Ask your interventional radiologist or vascular surgeon to develop a personalised health plan for healthy veins.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational and educational purposes only, and no medical advice should be taken from it. Always consult an interventional radiologist or vascular surgeon for treatment-related concerns or for health concerns you may have. Triage Meditech is not liable for any medical decision taken by any individual based on the contents of this article.
FAQs
What’s the fastest way to reduce varicose veins?
While complete removal requires medical intervention, elevating legs, wearing compression socks, and staying active can reduce symptoms quickly.
Are varicose veins permanent?
Not necessarily. Treatments like sclerotherapy or laser therapy can remove or reduce them, though new veins may form without lifestyle changes.
Can young people get varicose veins?
Yes, young adults can develop varicose veins, especially with genetic predispositions, pregnancy, or prolonged inactivity.
Is walking good for varicose veins?
Yes, walking improves circulation, strengthens leg muscles, and reduces symptoms of varicose veins.
Do varicose veins mean poor circulation?
Varicose veins often indicate venous insufficiency, a form of poor circulation, but they don’t always mean systemic circulatory issues.
How to Get Rid of Varicose Veins Naturally in 3 Minutes?
While eliminating varicose veins in 3 minutes isn’t possible, quick daily habits can reduce symptoms and improve vein health.
Quick Lifestyle Hacks
- Elevate Your Legs: Raise your legs above heart level for 3–5 minutes daily to improve blood flow.
- Stay Active: Short walks or leg exercises, like ankle pumps, boost circulation.
- Hydrate: Drinking water supports healthy blood flow and reduces swelling.
Natural Ingredients That Help
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Apply diluted apple cider vinegar to reduce inflammation and improve circulation.
- Horse Chestnut Extract: Known for reducing swelling and strengthening veins, available in creams or supplements.
- Ginger: Incorporate ginger tea to promote blood flow and reduce inflammation.