The body’s ability for regeneration and repair after an injury is demonstrated by wound healing. The body uses a series of complex and well-orchestrated biological mechanisms, whether it is a minor wound, a surgical scar, or chronic tissue damage, to restore the integrity of the tissues. Understanding these mechanisms highlights not only the wonders that are human physiology but also the importance of advanced solutions for wound care, such as those provided by leading MedTech firms. This blog will explore the stages in wound healing, tissue repair science, and modern medical interventions that enhance recovery.
What is Wound Healing?
Wound healing is a natural body response to tissue injury. It’s a cellular and biochemical response to fix the damage done. This is important to allow the natural protective layer of your skin to scalp recovery process, prevent infection, and maintain its health. The success of healing may be influenced by wound type (chronic or acute) and severity, as well as host medical status. NPWT may enhance wound healing in complex wounds by accelerating closure.
The Four Stages of Wound Healing
Wound healing occurs in four interrelated phases: hemostasis (clotting), inflammation (swelling), proliferation, and remodeling. Each phase has a specific role in repairing damaged tissue.
1. Hemostasis (Clotting) – Stop the bleeding
When an injury happens, the body immediately works to stop blood loss. In hemostasis, blood vessels contract to slow down circulation, and platelets collect at the injury in order to create a clot. This clot is mainly formed by fibrin and serves as a provisional seal while providing substrate for healing. This is an essential time because too much bleeding can slow healing and lead to infection.
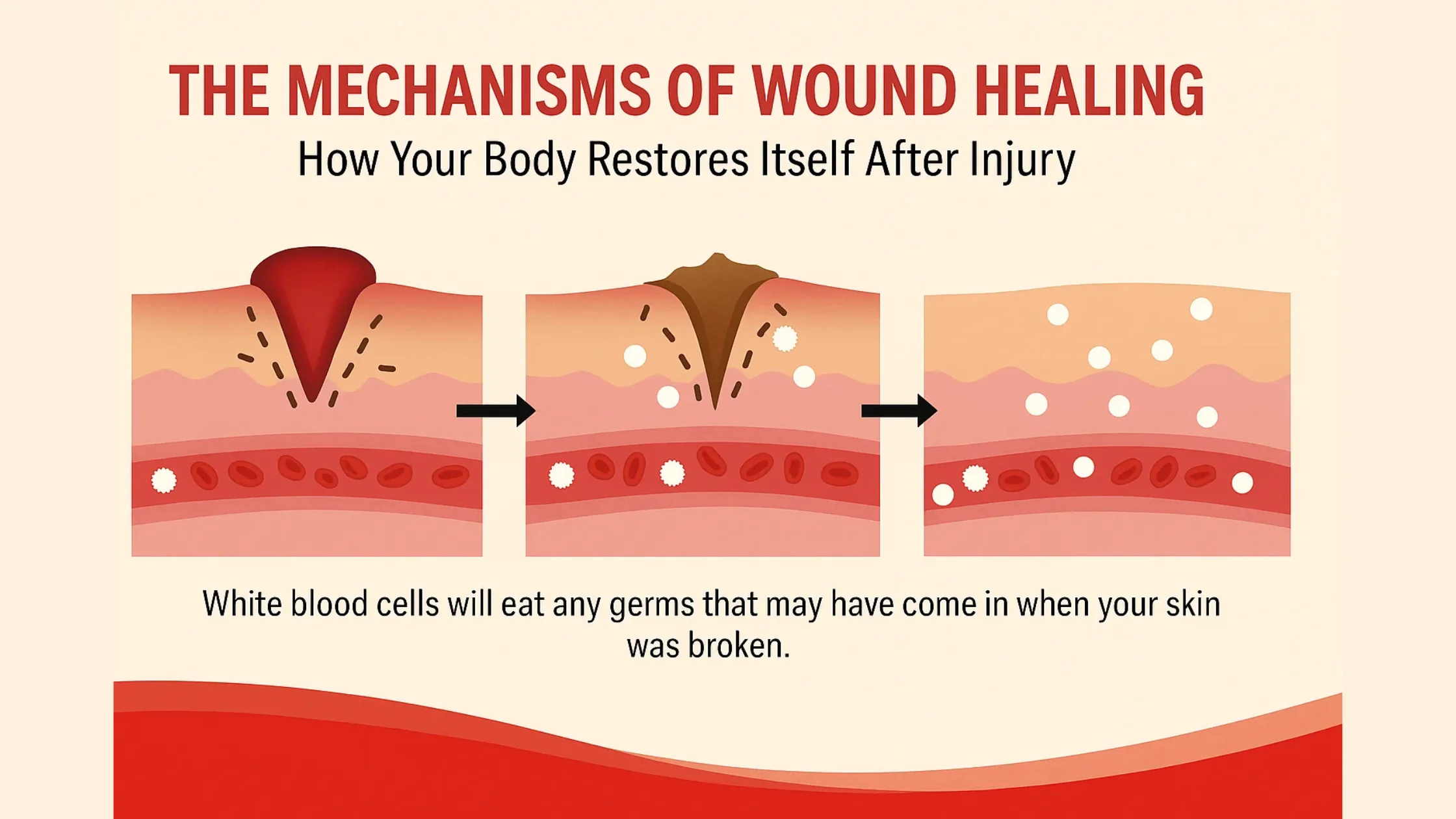
2. Inflammation (Swelling): Cleaning of the Wound
The inflammation phase is the body’s cleaning operation. It lasts between 1-4 days. White blood cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, rush to the area to remove bacteria, debris, and damaged tissue. The immune system is at work during this phase, which is marked by swelling, redness, and warmth. Although inflammation is necessary, excessive or prolonged inflammation can slow healing, particularly in chronic wounds such as diabetic ulcers.
Advanced Wound Care Solutions, including antimicrobial or NPWT solutions, can also assist in the management of inflammation and accelerate the process to promote efficient wound progression.
3. Proliferation – Rebuilding Tissue
The proliferative phase lasts from a few weeks to a few months and focuses on the rebuilding of damaged tissue. Fibroblasts are responsible for producing collagen, which is a protein that helps form the structure of new tissue. The development of new blood vessels (angiogenesis), which supply oxygen and nutrients to the wound, is accompanied by the migration of epithelial cells across the surface. This phase leads to the formation of pink, bumpy granulation tissue.
NPWT is a medical intervention that can speed up healing by accelerating proliferation. It does this by promoting tissue growth and blood flow.
4. Renovation: Strengthening Repair
The final phase of remodelling can last from months to years. The newly formed tissue is strengthened and matured during this phase. The collagen fibers are reorganized to increase tensile force, and the scars flatten and fade. The repaired tissue will never be as strong as uninjured skin. However, proper care in the earlier stages can optimize outcomes.
For chronic wounds such as surgical or pressure ulcers, advanced therapies may be required to promote remodelling and avoid complications, like scarring.
Factors Affecting Wound Healing
Many factors affect the speed and effectiveness of wound healing.
- Nutrition: Adequate zinc, vitamin A, and C, and protein are necessary for tissue repair.
- Infection: Bacterial contamination may delay healing and require antimicrobial intervention.
- Chronic Conditions: Diabetes, vascular diseases, and immune disorders can all impair the healing process, leading to chronic wounds.
- Age: Older people may heal more slowly due to a reduced cell turnover.
- Wound care: Cleaning, dressing, and advanced therapies such as NPWT improve recovery.
Understanding these factors, particularly in complex cases, is essential for surgeons and healthcare professionals to tailor treatments to patients.
Advanced Wound Care Technologies
Modern medical advances have revolutionised the management of wounds, especially for surgical or chronic wounds. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), for example, uses controlled suction in order to remove excess liquid, reduce swelling, and promote blood circulation, which accelerates healing. Companies such as Triage Meditech have been at the forefront in developing NPWT and wound care products. This has enabled surgeons to improve patient outcomes.
Bioactive dressings, growth factor therapy, and other innovations can further improve the body’s healing mechanisms. This is especially true in cases such as diabetic foot ulcers, burns, or even severe burns.
How to Support Wound Healing
Consider these tips to optimize wound healing:
- Cleanse the Wound: Wash the wound regularly with soap and water.
- Choose the Right Dressing: Use dressings that keep a moist atmosphere, as advised by healthcare professionals.
- Adhere to Medical Advice: Follow prescribed treatments for complex wounds such as NPWT and antibiotics.
- Maintaining a Healthy Diet: Consume foods rich in nutrients to support tissue healing.
- Do Not Smoke: Smoking slows the healing process.
Consultation with a healthcare provider, particularly for chronic or surgical injuries, will ensure personalised care and the best possible outcome.
Understanding Wound Healing is Important
Understanding the wound healing process allows patients to play a more active role in their recovery. This knowledge is crucial for surgeons and other medical professionals to make informed treatment decisions. This is especially true when using advanced technologies such as NPWT. Companies like Triage Meditech transform patient outcomes by combining cutting-edge wound solutions with the body’s natural repair mechanisms.
The science of wound-healing offers insight and hope for anyone who is recovering from an injury, whether it’s a minor one or a more complex one.