Case Study of Pressure Ulcer Using Negative Pressure Wound (NPWT) Therapy
Aim of Therapy:
MANAGEMENT OF PRESSURE ULCER USING NEGATIVE PRESSURE WOUND THERAPY
Patient Information:
| First Dressing Application Date: | 10/11/2022 |
| Dressing Remove Date: | 09/12/2022 |
| Patient Name: | Mr.Vikash |
| Patient Age: | 44-Year-Old |
| Wound Type: | Traumatic Wound |
| Exudates Type with Wound Depth: | Sero-Purulent drainage (2-3 Cm Deep Approx ) |
| Hospital Name: | Aiims Hospital ( Jodhpur ) |
| Doctor Name: | Dr.Satya Prakash |
| Doctor Specialty: | General Surgeon |
| Clinical Person Name: | Mr. Mahendra Prajapat |
| Patient Profile: | Surgical Wound |
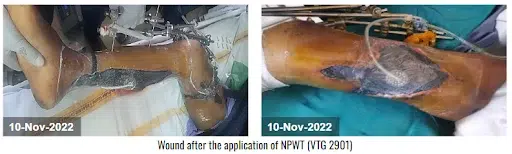
| Dressing Type/Device: | CCNPWT (VTG-2901) |
| Pressure Range: | -125mmHg |
| Any Major Illness During Therapy: | Fever And Body Pain |
| Diabetic / Non -Diabetic | Non-Diabetic |
| Supportive Ongoing Treatment | Antibiotics & Painkillers |
| Total Days of Recovery or Treatment Duration | 30 Days (5 Dressing Change) |
| Wound Location | Right Leg (Lower Extremity) |
Clinical Scenario:
A 44-year-old male patient was admitted to the hospital following an automobile accident in which he acquired a right leg injury resulting in a complex fracture. During the evaluation of the wound, he was diagnosed with compartment syndrome, which requires an emergency fasciotomy to relieve pressure from a damaged compartment in his right lower leg ( soleus muscle). After that, the patient underwent a surgical procedure. The patient was experiencing acute edema and numbness throughout his right thigh and lower leg. He was complaining of severe pain. After the evaluation of the wound, the doctor recommended CCNPWT (VTG 2901) for speedier wound healing.
Management:
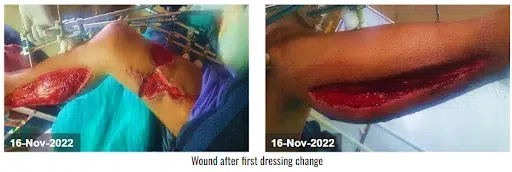
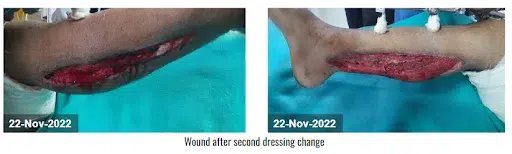
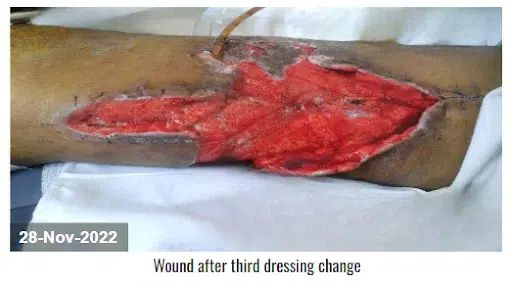
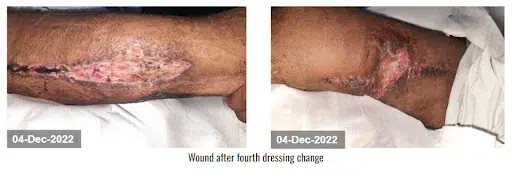
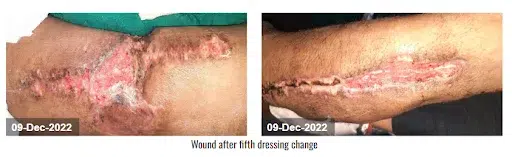
The devitalized tissue was removed with sharp debridement. CCNPWT (VTG 2901) was initiated at a pressure range of -125 mmHg for 7 days in a continuous pressure range. After the application of CCNPWT to the wound and 3 dressing changes, the wound surface was clean, there was no new necrosis, and tissue granulation was observed. After the fourth dressing change, the wound started to close progressively. It also removed the purulent discharge from the thigh and lower leg area, and it showed a well-circulated appearance. After the fifth dressing change, the edema of the right lower leg was reduced, 100% granulation tissue was formed on the wound bed, and the wound started to heal. After a satisfactory result, the doctor discontinued the device.